Hepatic steatosis: what it is and how to prevent it
Hepatic steatosis: a healthy liver is very important for the well-being of our organism. The liver, in fact, is a glandular organ connected to the digestive system that, with its action, participates in the digestion of the food we ingest. Its functions, moreover, are also associated with the defense of the organism and the elimination of harmful substances
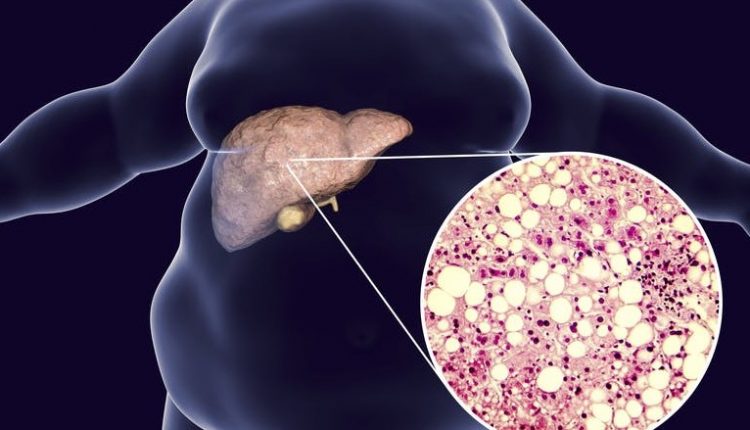
Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis, also known as “fatty liver”, is a rather common liver disease, which – according to estimates – affects more than 40% of the population. Steatosis can evolve into more severe conditions, such as liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
What is hepatic steatosis?
Hepatic steatosis is characterized by an accumulation of fat, in the form of triglycerides, in the cells of the liver.
Among the causes of hepatic steatosis are diabetes, sedentariness and a high-calorie diet.
Individuals who, therefore, are more likely to develop this disease are those who are overweight or have a body mass index greater than 30 and those who lead a particularly sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms of hepatic steatosis
Hepatic steatosis is a disease that generally manifests itself asymptomatically and, therefore, without the person affected being aware of it.
Steatosis, in fact, does not interrupt the normal functions of the liver, but can lead to hepatic fibrosis, i.e. an inflammation of the liver that involves a series of lesions that cause, in turn, the formation of fibrous tissue.
The fibrous tissue goes to interfere with the proper function of the liver, causing, in certain cases, cirrhosis.
Symptoms that the patient may experience at this stage of the disease are ascites, anemia, swollen legs, skin bleeding, fatigue and jaundice.
In addition, cirrhosis is a chronic and degenerative disease, which can give rise to liver tumors.
What tests for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis?
The pathology is initially suspected with an objective examination that takes into account the patient’s abdominal circumference.
It is also often related to the metabolic syndrome, which involves the concomitance of at least three factors: pre-diabetes, diabetes, obesity, hypertension and excess triglycerides.
Regarding, instead, the causes that lead to the development of fibrosis, instead, clarity has not yet been made.
There is no doubt that there is a genetic component, but also the diet is important in this process, especially when there is an excessive consumption of foods such as red meat, sausages, industrial sugars and trans and polyunsaturated fats.
The asymptomatic nature of hepatic steatosis implies that clinical controls are the main tools in the field of prevention.
We are therefore talking about blood tests, useful to assess the levels of liver enzymes, and examinations performed by diagnostic imaging.
It is also now available the fibroscan, a special test that recognizes the presence of liver fibrosis. Finally, a visit with a specialist is essential to assess the overall health of your liver.
Hepatic steatosis: lifestyle and prevention
Liver diseases can be prevented primarily by avoiding a sedentary lifestyle, practicing regular physical activity and following a balanced diet, rich in vegetable proteins, whole grains, fish and white meat, low in red meat and free of sweets and alcohol.
The Mediterranean diet is particularly indicated to decrease weight and reduce the amount of steatosis.
There are no drugs on the market able to block the degenerative process of non-alcoholic steatosis in liver fibrosis.
The modification of lifestyle is therefore a fundamental intervention and must pass through an improvement of diet, the regular practice of physical activity and the elimination of alcohol.
Read Also:
Acute Hepatitis And Kidney Injury Due To Energy Drink Consuption: Case Report
New York, Mount Sinai Researchers Publish Study On Liver Disease In World Trade Center Rescuers



