Monkeypox outbreak: What to know
Monkeypox outbreak: on the heels of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, a zoonotic virus seems to be spreading throughout Europe and into North America
Monkeypox has been making headway across the U.K., Spain, and Portugal since early May 2022
France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, and Australia have since confirmed at least one case in each country as well.
In the U.K., 20 monkeypox cases have been confirmed since early May.
During a press conference on May 17, World Health Organization (WHO) officials said that these are mostly separate occurrences except for “a family cluster with two confirmed cases and one probable case[…]”
Recently, Canada and the U.S. joined these nations in tracking and tracing the virus.
As of May 19, Canada confirmed two monkeypox cases and said it was investigating 17 suspected cases
The Massachusetts Department of Health also announced a single case in an individual who had recently been in Canada.
Several of the Canadian cases have been linked to this person.
On May 18, Scott Pauley, press officer at the Centers for Disease ControlTrusted Source (CDC), told:
“The U.K. notified the U.S. of 8 people in the U.S. who might have been seated near the U.K. traveler when they flew from Nigeria to London [on May 3-4, 2022].
Of these, one is no longer in the U.S., and one was not a contact.
The remaining six are being monitored by their respective state health departments.
None of these six travel contacts have monkeypox symptoms and their risk of infection is very low.”
The WHO officials have been tracking monkeypox’s path through Europe and North America for several weeks.
However, with the data available so far, they do not know long the virus has been spreading.
What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus, which transmits disease from animals to humans.
Cases typically occur near tropical rainforests, where animals that carry the virus live.
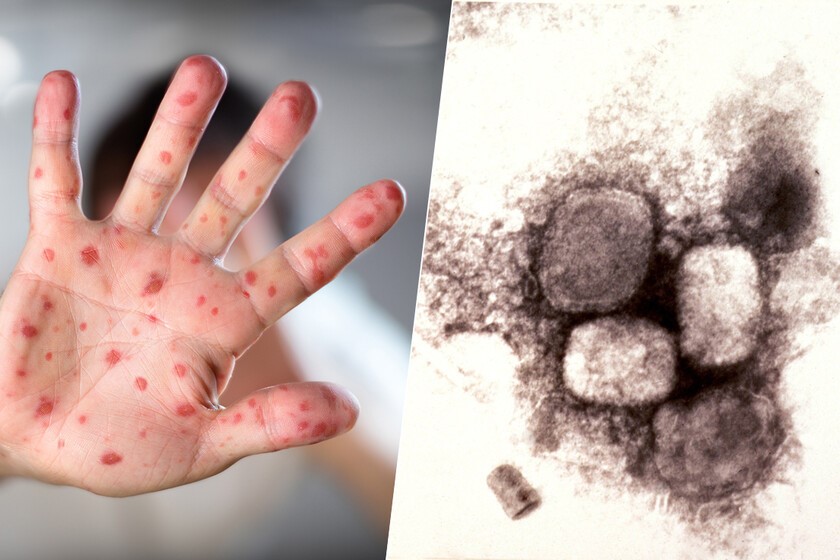
The monkeypox virus is a member of the orthopoxvirus family.
It also has two distinct genetic strains or clades: the Central African (Congo Basin) clade and the West African clade.
The Congo Basin clade is known to spread more easily and cause more severe symptoms.
Monkeypox naturally occurs in Africa, especially in west and central African nations.
Cases in the U.S. are rare and associated with international travel from places where the disease is more common.
Monkeypox, what are the symptoms?
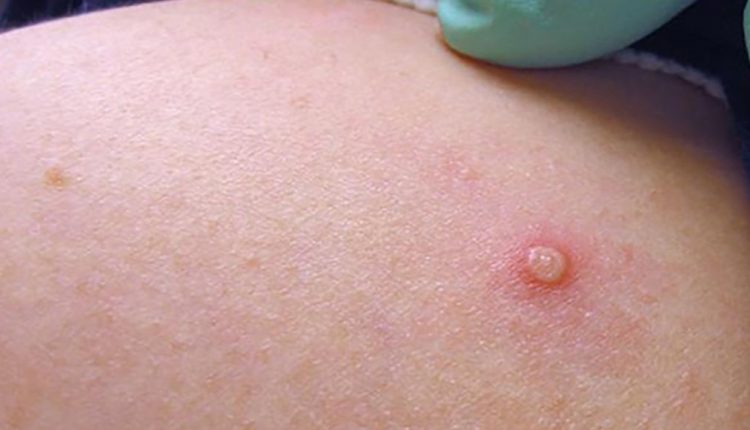
Monkeypox symptoms and signs include headache, skin rash, fever, body aches, chills, swollen lymph nodes, and exhaustion.
It produces symptoms similar to smallpox, but milder.
The time from infection to the onset of symptoms, which is referred to as the incubation period, can range from five to 21 days.
The illness typically resolves within two to four weeks.
Severe cases are more common among people with underlying immune deficiencies and young children.
In recent times, the case fatality ratioTrusted Source of monkeypox is around 3-6%.
How is it transmitted?
Transmission of the monkeypox virus among humans is limited, but it can happen through close skin contact, air droplets, bodily fluids, and virus-contaminated objects.
Most of the recent cases of monkeypox in the U.K. and Canada have been reported among attendees of sexual health services at health clinics in men who have sex with men.
Regarding this trend, Dr. I. Socé Fall, the regional emergencies director for the WHO’s Health Emergencies Program, cautioned:
“This is new information we need to investigate properly to understand better the dynamic of local transmission in the U.K. and some other countries.”
Many unknowns about the latest cases
During a press conference on May 17, Dr. Fall acknowledged that public health officials still have much to learn about the monkeypox virus.
“But the most important thing is we really need to invest in understanding the development of monkeypox because we have so many unknowns in terms of the dynamics of transmission, the clinical features, the epidemiology. In terms of therapeutics and diagnostics also, we still have important gaps,” he said.
WHO experts believe that solutions for monkeypox calls must go beyond addressing the disease
During the press conference, Dr. Michael RyanTrusted Source, executive director of the WHO’s Health Emergencies Program, said: “Getting answers isn’t just about getting answers about the virus.
We’ve got to get answers about the hosts, we’ve got to get answers about human behavior and practice, and we’ve got to operate at all levels to try and ensure that human populations are protected.”
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
HIV Evolving ‘Into Milder Form’
Managing Chickenpox In Children: What To Know And How To Act
Monkeypox Virus: Origin, Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention Of Monkey Pox
Monkeypox: Genesis, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment