Basic trauma life support (BTLS) : here are the procedures to adopt
Basic Trauma Life Support (BTLS) refers to the set of practices used in first aid for people who have suffered trauma and are in a state of shock, with injuries, in cases of polytrauma or unconsciousness
The quicker you contact first responders capable of implementing BTLS (no more than sixty minutes), the more likely the traumatised person is to recover.
BTLS, Contacting Rescue
The best way to initiate the BTLS procedure starts with the call to the emergency number, which is made to request help; if during this call the person is able to define the trauma and the situation in the best possible way, help will arrive already equipped in an adequate and efficient way, saving precious time.
Therefore, in the call, the caller must indicate: the patient’s age, the dynamics of the accident or illness (in the case of a car accident, which vehicles collided, whether there were any fatalities, and whether the persons involved were thrown from the vehicle or remained inside); in the case of a fall, estimate the approximate height; in the case of trauma, burns or illness, define the possible cause, the symptoms, any chronic disorders and the time elapsed.
It is very important to define the damage, which can be primary or secondary:
– Primary damage includes fractures and ruptured ligaments;
– Secondary damage includes trauma to internal organs, hypoxia, hypotension, hypercapnia and hypothermia.
The chain of survival
The chain of survival is the concatenation of actions that quickly trigger the rescue phase: 1. Call the emergency number 2.
Early start of intensive care
Basic Trauma Life Support (BTLS)
Before providing aid, the rescuer generally considers the scene, ensuring that there are no sources of gas, electrical wires, or flammable liquids that could impede the procedure.
An assessment of the patient’s state of consciousness and of the damage sustained is then carried out; if it is a question of trauma and not of illness, it is advisable not to move the subject. However, in cases where the patient is unconscious and therefore it is not possible to assess whether there has been a malfunction or an accident, it is necessary to proceed as in the case of a trauma.
Therefore, first of all the patient’s state of consciousness is assessed through the sensory response, then the person is called and touched; if the person does not react, he or she is unconscious and the SVT is performed.
BTLS: procedure
The Trauma Life Support protocol consists of five points:
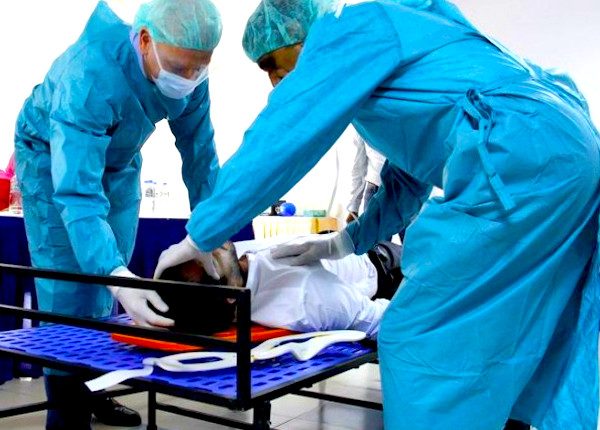
– Airway and Spine Control: immobilise the head and apply the collar, if the patient is unresponsive check the airway and if necessary tracheotomy;
– Breathing: assessing whether breathing is present or absent; in the case of the latter, ventilation is carried out (self-expanding balloon connected to the oxygen cylinder); in the case of the former, a mask is placed on the patient and oxygen is delivered, then OPACS is carried out: observation, palpation of the chest, listening to breathing, counting the respiratory rate and oxygen saturation in the blood;
– Circulation: phase in which the heartbeat is checked by means of the carotid pulse; if there is no pulse, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed with 12 insufflations per minute with the self-expanding balloon connected to the oxygen cylinder, then the pressure is checked with the sphygmomanometer;
– Disability: the subject’s neurological state is checked by assessing whether he or she is alert, lucid, and responds to verbal and pain stimuli; the severity of the damage is assessed on the basis of the response;
– Exposure: in the case of injuries, the subject is undressed and the severity of the injuries and the mobility of the limbs is assessed, or in the case of hypothermia, the subject is covered with a thermal blanket.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
European Resuscitation Council (ERC), The 2021 Guidelines: BLS – Basic Life Support
Safety Of Basic Life Support (BLS-D) Courses In The COVID Era: A Pilot Study
Manual Ventilation, 5 Things To Keep In Mind
Ambu Bag: Characteristics And How To Use The Self-Expanding Balloon



