Bacterial endocarditis: prophylaxis in children and adults
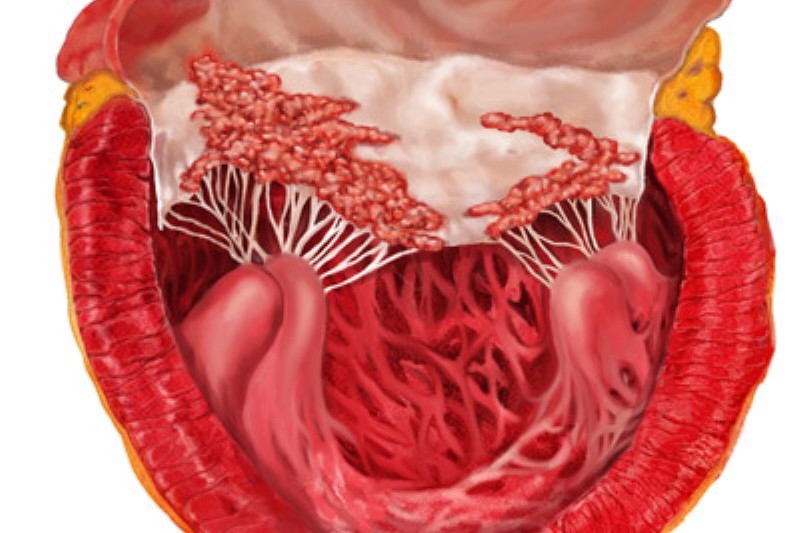
Bacterial endocarditis is an infection of the internal structures of the heart or large arteries caused ‘by the implantation’ of bacteria or, more rarely, fungi
The passage of germs into the bloodstream can be caused by foci of infection wherever they are located, by surgical operations, obstetrical-gynaecological procedures and instrumental manoeuvres capable of causing bleeding, particularly if performed in areas habitually rich in bacterial flora such as the oral cavity, the genito-urinary tract, the upper respiratory tract or the gastrointestinal tract.
Particularly at risk of contracting bacterial endocarditis are patients with congenital cardiac malformations, acquired valvular defects or the outcomes of cardiac surgery (artificial or biological prostheses, valves, patches).
It should be emphasised that prophylaxis of rheumatic disease using Penicillin in ‘delayed’ form does not prevent bacterial endocarditis.
BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS PROPHYLAXIS
General recommendations:
- Maintain good oral hygiene and have regular dental check-ups
- Promptly report any febrile episode without an obvious cause to your doctor
- Carry this printout with you and show it to your dentist, surgeon or other specialist before your visit
ADULTS
Dental and upper airway procedures
A) Oral:
- First choice: Zimox or Velamox 3 grams 1 hour before and 1.5 grams 6 hours after the procedure.
- Penicillin allergic persons: Erythrocin 1 gram 2 hours before and 500 mg 6 hours after.
B) Parenteral route:
- First choice: Amplital 2 grams in muscle or IV 30 minutes before + Gentalyn 1.5mg/Kg in muscle or ev 30 minutes before.
- Penicillin allergy sufferers: Vancomycin 1 gram intravenously over 1 hour slowly (starting 1 hour before the procedure)
Gastrointestinal and genitourinary procedures:
A) Oral:
- Zimox or Velamox 3 grams 1 hour before and 1.5 grams 6 hours after the procedure.
B) Parenteral route:
- First choice: Amplital 2 grams in muscle or IV 30 minutes before + Gentalyn 1.5mg/Kg in muscle or IV 30 minutes before.
- Penicillin allergy sufferers: Vancomycin 1 gram intravenously over 1 hour slowly (starting 1 hour before the procedure)+ Gentalyn 1.5mg/Kg in muscle or intravenously 30 minutes before.
CHILDREN
Dental and upper airway procedures
A) Oral:
- First choice: Zimox or Velamox 50 mg/Kg 1 hour before and 25 mg/kg 6 hours after the procedure
- Allergic to Penicillin: Erythrocin 20 mg/Kg 2 hours before and 10 mg/Kg 6 hours after
B) Parenteral route:
- First choice: Amplital 50mg/Kg in muscle or IV 30 minutes before + Gentalyn 2 mg/Kg in muscle or IV 30 minutes before
- Penicillin allergy sufferers: Vancomycin 20mg/Kg intravenously over 1 hour slowly infused (thus starting 1 hour before the procedure)
Gastrointestinal and genitourinary procedures:
a) Oral:
- First choice : Zimox or Velamox 50mg/Kg 1 hour before and 25 mg/Kg 6 hours after the procedure.
b) Parenteral route:
- First choice: Amplital 50 mg/Kg in muscle or IV 30 minutes before + Gentalyn 2 mg/Kg in muscle or IV 30 minutes before.
- Penicillin allergy sufferers: Vancomycin 20 mg/Kg infused slowly over 1 hour (thus starting 1 hour before the procedure) + Gentalyn 2 mg/Kg in muscle or intravenously 30 minutes before.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Defibrillator: What It Is, How It Works, Price, Voltage, Manual And External
The Patient’s ECG: How To Read An Electrocardiogram In A Simple Way
Signs And Symptoms Of Sudden Cardiac Arrest: How To Tell If Someone Needs CPR
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Quickly Finding – And Treating – The Cause Of A Stroke May Prevent More: New Guidelines
Atrial Fibrillation: Symptoms To Watch Out For
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: What It Is And How To Treat It
Do You Have Episodes Of Sudden Tachycardia? You May Suffer From Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
Transient Tachypnoea Of The Newborn: Overview Of Neonatal Wet Lung Syndrome
Tachycardia: Is There A Risk Of Arrhythmia? What Differences Exist Between The Two?