DBS - Deep Brain Stimulation: what it is and when it is needed
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment aimed at reducing debilitating motor symptoms characteristic of movement disorders such as Parkinson’s, dystonia and essential tremor
This procedure is also used to treat epilepsy, chronic pain and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
What is deep brain stimulation?
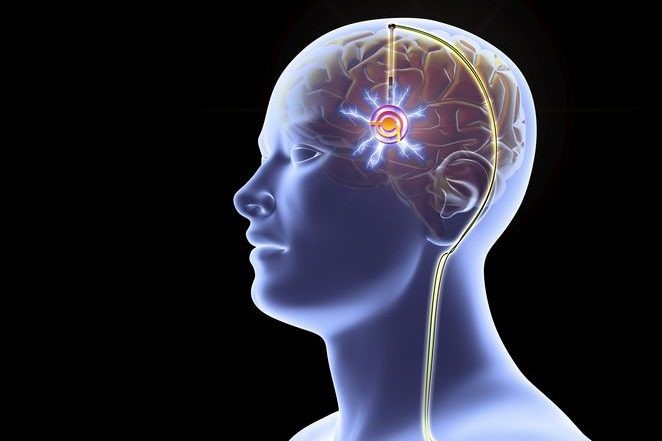
The treatment consists of surgically implanting leads in the areas of the brain responsible for controlling movement, and, in addition, a medical device, similar to a cardiac pacemaker, near the collarbone or in the abdominal region.
The latter sends electrical impulses to electrodes located in the brain areas, blocking the signals that cause the disabling motor symptoms.
Patients are thus able to experience an improvement in their clinical picture.
In addition, the device can be controlled wirelessly via an external programmer that allows the stimulation parameters to be adjusted, or the device to be switched off if necessary.
Deep brain stimulation is an invasive surgical procedure
It involves drilling through the skull under local anaesthesia.
Electrodes are then inserted deep into the brain to identify by means of clinical and neurophysiological tests (the patient is asked, for example, to open and close his or her hand) the area in which the definitive electrode is to be inserted.
This method has been used to treat Parkinson’s disease for over 20 years and the data collected show that this technique offers good, in some cases excellent, results, provided that patients are carefully selected.
Which patients can undergo the treatment?
The procedure is indicated in patients with Parkinson’s disease who have motor fluctuations and dyskinesias that can no longer be controlled by pharmacological treatment.
Subjects who can undergo this therapy make up about 10% of the population with Parkinson’s disease.
They are relatively young and healthy subjects (age limit 70 years), with severe side effects from the drug therapy used to control the disease.
They must still have a positive response to levodopa administration, even if it is short-lived.
Intact cognitive and mental functions and normal neuroradiological imaging are required.
Follow up
After 2-3 weeks after surgery, when the clinical picture appears sufficiently stable and an initial stimulator adjustment has been made, the patient can be discharged.
He will have to perform outpatient check-ups in the following months to make any changes in the stimulation parameters and adjust the drug therapy.
The improvement of Parkinson’s symptoms is already evident in the first few days after starting stimulation.
This allows the dose of dopaminergic medication to be reduced by 50 to 80 per cent, with around 15 to 20 per cent of patients not needing the therapy.
Deep brain stimulation, are there any preparation rules for treatment?
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a thorough clinical examination using the Parkinson’s disease assessment scale: the patient is assessed according to his mental state, activities of daily living, motor functions, complications due to the therapy, and the progression and stage of the disease.
In addition, special emphasis is placed on the assessment of tremor, rigidity, akinesia and balance disorders.
The analysis is carried out both during drug therapy and after its discontinuation.
Based on the assessment and the prevalence of one of the symptoms over the others, the brain region in which the lead is to be implanted is chosen.
Further pre-implantation preparation consists in carrying out investigations prior to surgery: blood tests, chest X-ray, ECG, skull X-ray, CT scan or MRI of the brain.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Tourette Syndrome: Symptoms And How To Treat It
Dementia, Hypertension Linked To COVID-19 In Parkinson’s Disease
Relationship Between Parkinson’s And Covid: The Italian Society Of Neurology Provides Clarity
Parkinson’s Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment