Paediatrics, how to deal with scabies in paediatric age
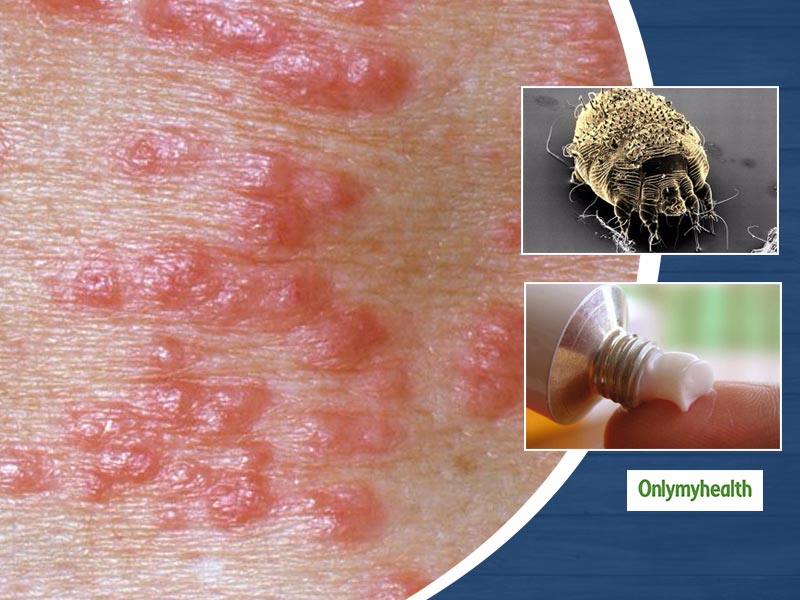
Scabies is a skin disease due to a parasite specific to humans, a small mite (0.4 – 0.3 mm), invisible to the naked eye, called Sarcoptes scabiei variant hominis
Scabies is not a particularly dangerous disease, but its characteristic feature is its high contagiousness both through direct physical contact with the infected person and through personal objects.
It is therefore essential to initiate treatment and disinfection of rooms and clothing (including sheets and towels) promptly to prevent its spread within the family, work or care home.
Characteristic symptoms and signs of scabies are:
– intense itching (mainly at night)
– small red blisters or blisters especially at the level of the skin folds, sometimes accompanied by fine tracks or lines, which are the tunnels dug by the parasite called scabious burrows
– scratching lesions mainly on the interdigital spaces, palms and soles, wrists, ankles, armpits, groin, genitals, hips
The diagnosis of scabies involves a thorough test of the skin by the treating physician, who will look for signs of the presence of the parasite to allow early identification of the disease and the timely initiation of treatment, which are essential to reduce the spread of the infestation.
In cases of doubt, the practitioner may request a dermatological examination.
The treatment of scabies is aimed at eliminating the parasites using medicines mainly in the form of creams
Recently, an increasing inefficacy of first-line therapies (topical permethrin) has been noted, as treatment is not always carried out correctly, with the consequent need to resort to galenic preparations with other active ingredients (e.g. benzyl benzoate, sulphur derivatives), which are more expensive and not always dispensed by the National Health Service.
In order to contain contagions, in addition to disinfecting rooms, clothing, linen and objects, it is strongly recommended that the therapy be carried out by the whole family contacting the case.
This entails, in some cases, financial difficulties for families in carrying out the course of treatment, which must be performed synchronously in all intimate contacts of the affected patient, applying a cream to the entire body.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Classification Of Skin Lesions
Atopic Dermatitis: Treatment And Cure
Allergic Contact Dermatitis And Atopic Dermatitis: The Differences
Managing Chickenpox In Children: What To Know And How To Act
Monkeypox Virus: Origin, Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention Of Monkey Pox
What Are The Symptoms Of Monkeypox?
Scabies: Symptoms And Treatment Of Sarcoptes Scabiei Infection
Eczema, Rash, Erythema Or Dermatosis: Let’s Talk About Our Skin
Hyperchromia, Dyschromia, Hypochromia: Skin Color Alterations
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Definition, Causes And Treatment
Dermatosis: Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
Allergic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment And Prevention


