Carotid stenosis: what is it and what are the symptoms?
Carotid artery stenosis is a condition whereby a narrowing of the carotid artery causes reduced blood flow to the brain, with the risk that the patient will suffer major brain diseases
Early diagnosis is essential to avoid the onset of diseases such as stroke.
Carotid stenosis – what causes it?
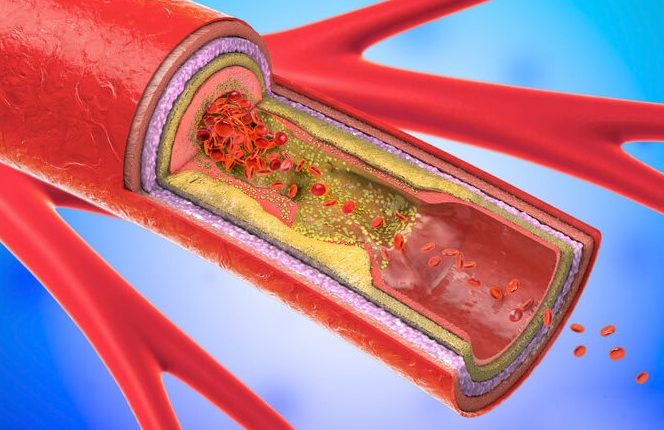
Carotid stenosis is characterised by the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques (i.e. aggregates of cholesterol, calcium, disordered fibromyocytes and inflammatory cells) in the vessel wall, which progressively grow until they occupy the entire lumen of the artery.
Those most at risk of carotid stenosis are patients over 60 years of age who have vascular risk factors.
DEFIBRILLATORS, VISIT THE EMD112 BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
The most common risk factors for carotid steatosis include:
– arterial hypertension
– hypercholesterolemia
– diabetes mellitus
– obesity
– male sex
– smoking
– family history of ischaemic events.
Carotid stenosis, what are the symptoms?
If a portion of the atherosclerotic plaque ruptures, its fragments follow the blood flow and cause embolisation with occlusion of a cerebral vessel.
The result is a cerebral infarction, which may manifest itself in the form of a transient ischaemic attack (TIA), with acute neurological symptoms that recede within a few minutes or a few hours; in the most serious cases, a full-blown stroke may occur.
These same phenomena can also occur as a result of acute complete carotid artery obstruction, which can occur as a result of progressive plaque growth.
More than 90% of patients are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis, allowing the specialist to intervene before brain damage occurs.
Is it possible to prevent stroke?
It is possible to prevent ischemic stroke by adopting a series of good rules that can correct modifiable risk factors, such as smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and by undergoing an echocolordoppler examination of the supra-aortic trunks, especially in the case of subjects at risk.
This examination allows precise visualisation of even the smallest plaques, making it possible to monitor them over time and correct them in the most serious cases. It is a fast, non-invasive examination that does not require the use of contrast medium.
DEFIBRILLATORS OF EXCELLENCE IN THE WORLD: VISIT THE ZOLL STAND AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Carotid stenosis: can it be cured?
In cases where the echocolordoppler examination shows a critical plaque or a plaque at risk, even if the patient is asymptomatic, it is necessary to opt for a carotid thromboendoarteriectomy (TEA) or carotid stenting (PTA) surgery.
Both of these operations are generally performed under local anaesthesia and require a short stay in hospital, and can provide an effective and lasting solution to the condition, while minimising the risk of stroke.
The choice of treatment must take into account several factors and is made on a case-by-case basis according to the patient’s characteristics and needs.
Read Also:
Coronary Angioplasty, What To Do Post-Operatively?
Heart Patients And Heat: Cardiologist’s Advice For A Safe Summer
US EMS Rescuers To Be Assisted By Paediatricians Through Virtual Reality (VR)
Silent Heart Attack: What Is Silent Myocardial Infarction And What Does It Entail?
Mitral Valve Diseases, The Advantages Of Mitral Valve Repair Surgery
Coronary Angioplasty, How Is The Procedure Performed?



