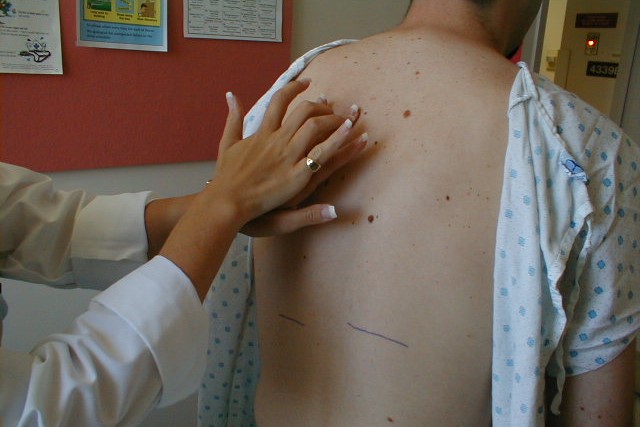
Objective examination: what is percussion and why is it done?
Percussion is a method of semeiotics in medicine that consists of drumming (with two fingers over an interposed middle finger) on the body surface to investigate underlying structures, and is therefore used in the objective examination to assess the condition of the chest and abdomen
Percussion is one of the four classic methods of clinical examination, along with inspection, palpation and auscultation
It is performed with the middle finger of one hand drumming on the middle finger of the other hand, which is placed firme on the skin covering the soft tissue, never on the bone.
There are two types of percussion: direct, which uses one or two fingers, and indirect, which uses the middle finger as a flexor.
There are four types of percussion sounds: resonant, hyper-resonant, obtuse thigh sound or obtuse.
An obtuse ‘thigh’ sound indicates the presence of a solid mass under the surface of the skin/tendonous fasciae/muscle plateau/peritoneum.
A more booming sound indicates empty cavities containing air.
Percussion had been used for centuries to distinguish between full and empty barrels of liquor, wine and beer, and Dr. Joseph Leopold Auenbrugger was inspired by this technique for medical percussion.
Percussion of the chest
It is used to diagnose cardiac hypertrophy, pneumothorax, emphysema and other diseases.
It can be used to establish respiratory mobility of the thorax.
Percussion of the abdomen
It is used to detect whether an organ shows an enlarged and/or altered ‘aia’ (projection surface towards the skin) in sounds.
It is based on the principle of discriminating between tissues and the gaps between them by the vibrations that the tissues emit upon percussion.
The sound generated is used to determine whether the size and nature of the underlying tissue is normal (and therefore likely healthy) or abnormal, suggesting an underlying pathology to be investigated with further procedures.
Percussion of the abdomen is useful to detect:
- Ascites
- Cardiomegaly (although nowadays echocardiography or the old Rx telecore is preferred)
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen)
Percussion notes
Based on tactile and auditory perception, the tones/notes that are heard can be categorised as:
- Tympanic;
- Hyper-resonant (in the pneumothorax);
- Normal Resonance / Resonant;
- Reduced resonance (underlying masses, consolidation-fibrosis of lung tissue);
- Obtuse (consolidation);
- Hard obtuseness, ‘thigh sound’ (in pleural effusion).
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Palpation In The Objective Examination: What Is It And What Is It For?
Heart Disease: What Is Cardiomyopathy?
Auscultation In The Objective Examination: What Is It And What Is It For?
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Heart Murmurs: What It Is And When To Be Concerned
Broken Heart Syndrome Is On The Rise: We Know Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
What Is A Cardioverter? Implantable Defibrillator Overview
Cardiomyopathies: What They Are And What Are The Treatments



