Raynaud's syndrome: symptoms, causes and treatment
Raynaud’s syndrome is a phenomenon caused by sudden, transient vasospasms of the arteries in the fingers of the hand
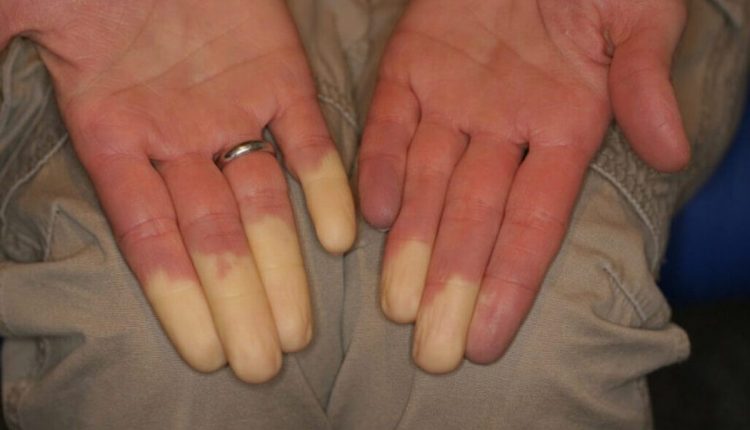
This vasoconstriction leads to a transient ischaemia resulting in a paleness of certain areas of the fingers lasting a few minutes, followed by an intense reactive vasodilation with redness.
In some cases, the crises follow one another so intensely that they also cause very painful ulcerations.
Raynaud’s syndrome: the symptoms
Pallour is associated with pain, ‘ants’ and ‘dead finger’ sensations, which are very unpleasant for the patient.
Seizures generally occur with exposure to cold and are more frequent in winter, but sometimes occur spontaneously.
In some milder forms there are one or two crises per year, other times several crises within the same day.
The causes of Raynaud’s syndrome
There are several causes. First of all, one must distinguish some familiar forms, spontaneous and without an apparent cause, generally not very annoying, often limited to one or two fingers, with a benign course, from other pathological forms of which Raynaud’s is only an indicator:
- scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- ergotamine intoxication;
- upper thoracic stricture syndrome;
- cryoglobulinemia;
- cervical arthrosis;
- neoplasms.
In any case, an angiological and immunological examination, followed by blood and instrumental tests (dynamic arterial echodoppler of the upper limbs, capillaroscopy) can make the differential diagnosis and set therapy.
Sometimes it is necessary to perform a small biopsy of the fingertip in order to obtain data of safe interpretation.
Care and treatment of Raynaud’s syndrome
Therapy for Raynaud’s syndrome is carried out in cases that are bothersome due to the number and intensity of crises.
A distinction is made between local therapies (creams, topical preparations) and general therapies (drugs), whichare able to alleviate and reduce crises.
In rare cases, surgery (thoracic sympathectomy) is indicated, especially when ulcerations or crises of such intensity as to be disabling coexist.
If present, immunological pathologies must obviously also be treated.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Paresthesias: Meaning, Causes, Risks, Diagnosis, Cures, Remedies, Exercises
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Exposure To Cold And Symptoms Of Raynaud’s Syndrome
Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment



