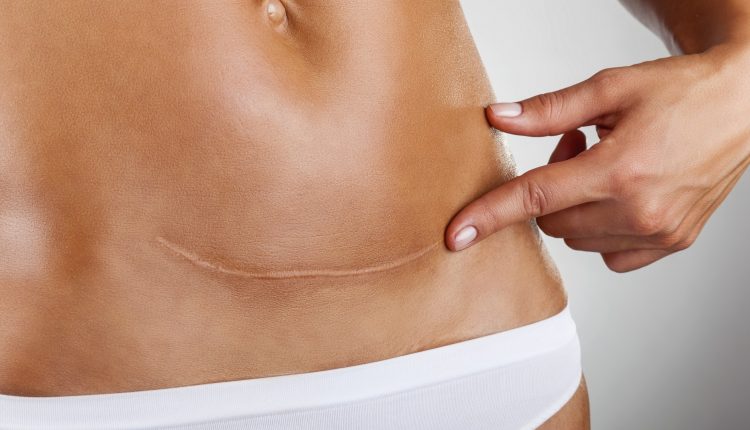
What is abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty is a plastic or cosmetic surgery procedure to strengthen the muscles in case of abnormalities such as diastasis or to improve the appearance of the abdomen by removing excess skin and fat in the abdominal area
FOR WHOM IS ABDOMINOPLASTY INDICATED?
Abdominoplasty is used to reshape the abdomen and remove excess skin tissue formed as a result of heavy weight loss, pregnancy or age-induced skin relaxation. In these cases, skin folds and folds can form, causing dermatitis, difficulty of movement and psychological discomfort.
It is also indicated in cases of abdominal diastasis, i.e. the estrangement between the right and left fascia of the rectus abdominis muscle, a consequence of pregnancies, excessive exertion, and obesity.
HOW IS ABDOMINOPLASTY PERFORMED?
Abdominoplasty can be performed using different techniques, depending on the size of the areas to be treated.
Before proceeding with the operation, the plastic surgeon clearly explains which procedure he intends to use, how and where the scars will be and what results can be achieved.
Generally, incisions are made between the navel and the pubis, with the extent varying according to the case.
Skin and fat are then ‘peeled off’ from the muscle bands, the excess is removed and, if necessary, the belly button is repositioned.
In the case of diastasis of the muscles, sutures or the insertion of support nets are used.
At the end of the operation, catheters are inserted to drain fluid.
Sutures are performed as far as possible with internal stitches to minimise scarring.
The operation, which can last between two and four hours, is mostly performed under general anaesthesia.
WHAT IS POST-OPERATIVE RECOVERY LIKE?
After abdominoplasty it is normal for the abdomen to be sore for a few weeks and for bruising and swelling to be present.
In the days following the operation it is important to follow all the doctor’s instructions and wear a compression sleeve if prescribed.
The convalescence period lasts about four weeks, during which exertion, twisting of the trunk and sporting activities should be avoided.
Regular post-operative check-ups are necessary until complete recovery.
IS ABDOMINOPLASTY SURGERY CONCLUSIVE?
The aesthetic improvement after abdominoplasty is immediately visible, but it takes about six months of settling in to achieve the final result.
Sometimes, surgery may be necessary after this period to correct any remaining imperfections.
Ageing, possible pregnancies after surgery and major weight changes can lead to changes in the appearance of the abdomen.
ARE THERE ANY CONTRAINDICATIONS?
Abdominoplasty is contraindicated in cases of severe chronic heart, lung and liver disease, diabetes, obesity (body mass index greater than 30), and smoking.
In addition, the weight must be kept as stable as possible after the operation: it should therefore not be performed before or during a weight-loss diet, but only after the desired weight has been reached.
It is also contraindicated in women who wish to become pregnant.
Finally, it is not advisable if previous abdominal surgery has resulted in the growth of too much scar tissue (keloids).
WHAT CAN BE THE RISKS OF ABDOMINOPLASTY?
Like any surgical procedure, abdominoplasty involves, albeit rarely, certain risks, such as adverse reactions to anaesthesia, bleeding, infection, haematomas, accumulation of fluid in the tissue (seroma), difficulty in wound healing and the formation of blood clots (thromboembolism).
To these can be added complications specific to abdominoplasty, such as necrosis of abdominal fat tissue, skin necrosis and navel necrosis.
A change in skin sensitivity of the abdomen is also possible, which may be transient or permanent.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Umbilical Cord: What Is It, What Is It For, What Does It Contain?
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck): What It Is And When It Is Performed
Abdominal Bloating? The Breath Test Can Identify The Causes
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
What’s Causing Your Abdominal Pain And How To Treat It
Intestinal Infections: How Is Dientamoeba Fragilis Infection Contracted?
Early Parenteral Nutrition Support Cuts Infections After Major Abdominal Surgery
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Abdominal Trauma: A General Overview Of Management And Trauma Areas
Abdominal Distension (Distended Abdomen): What It Is And What It Is Caused By



