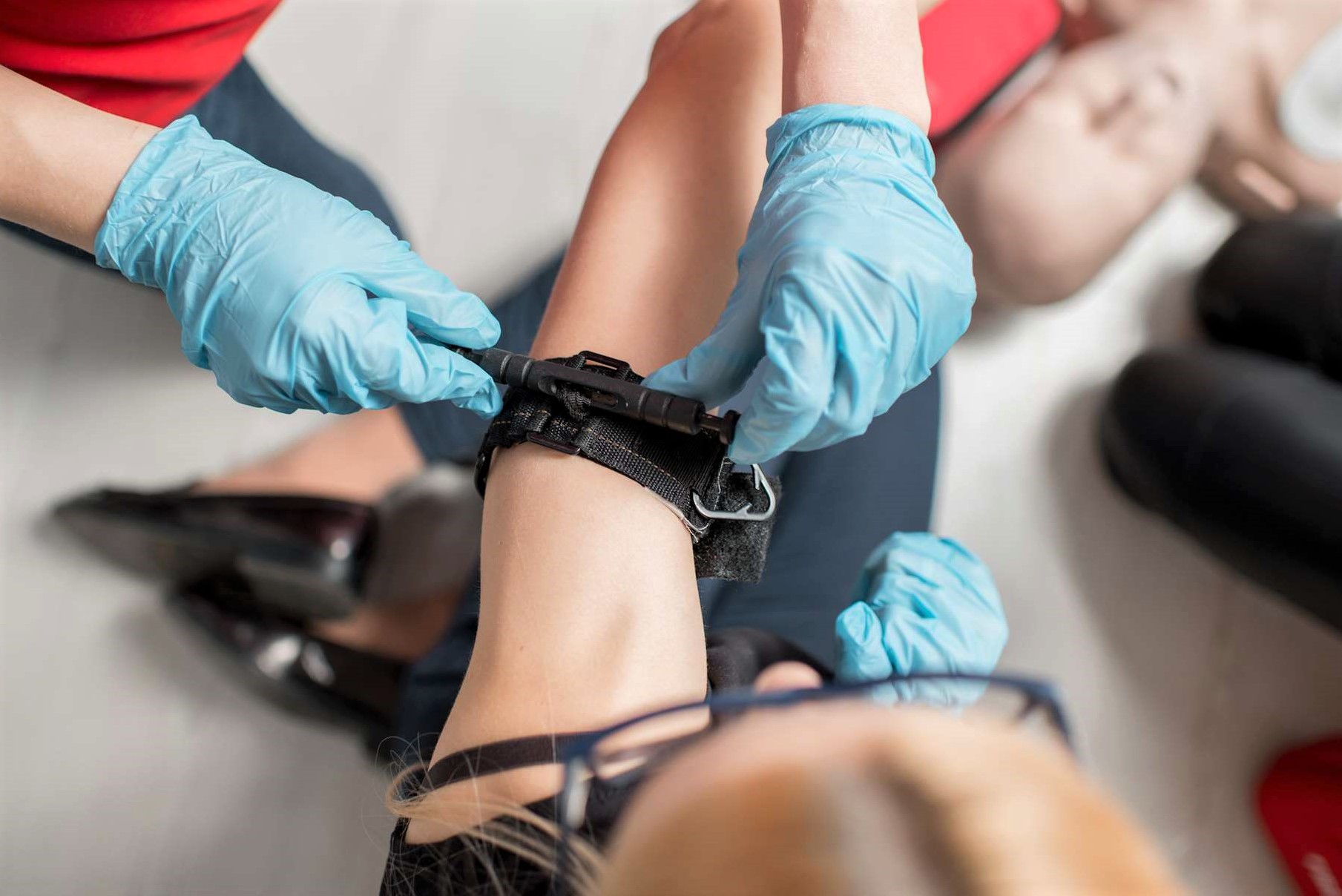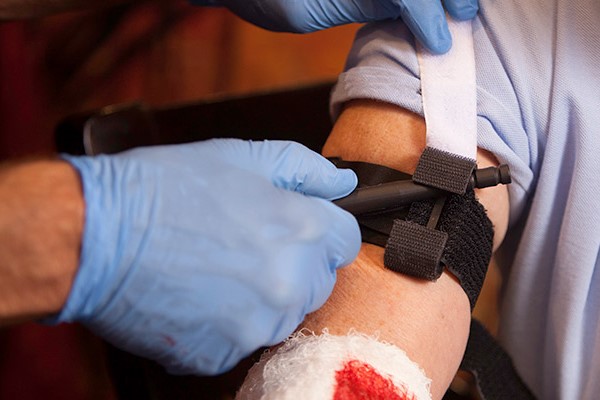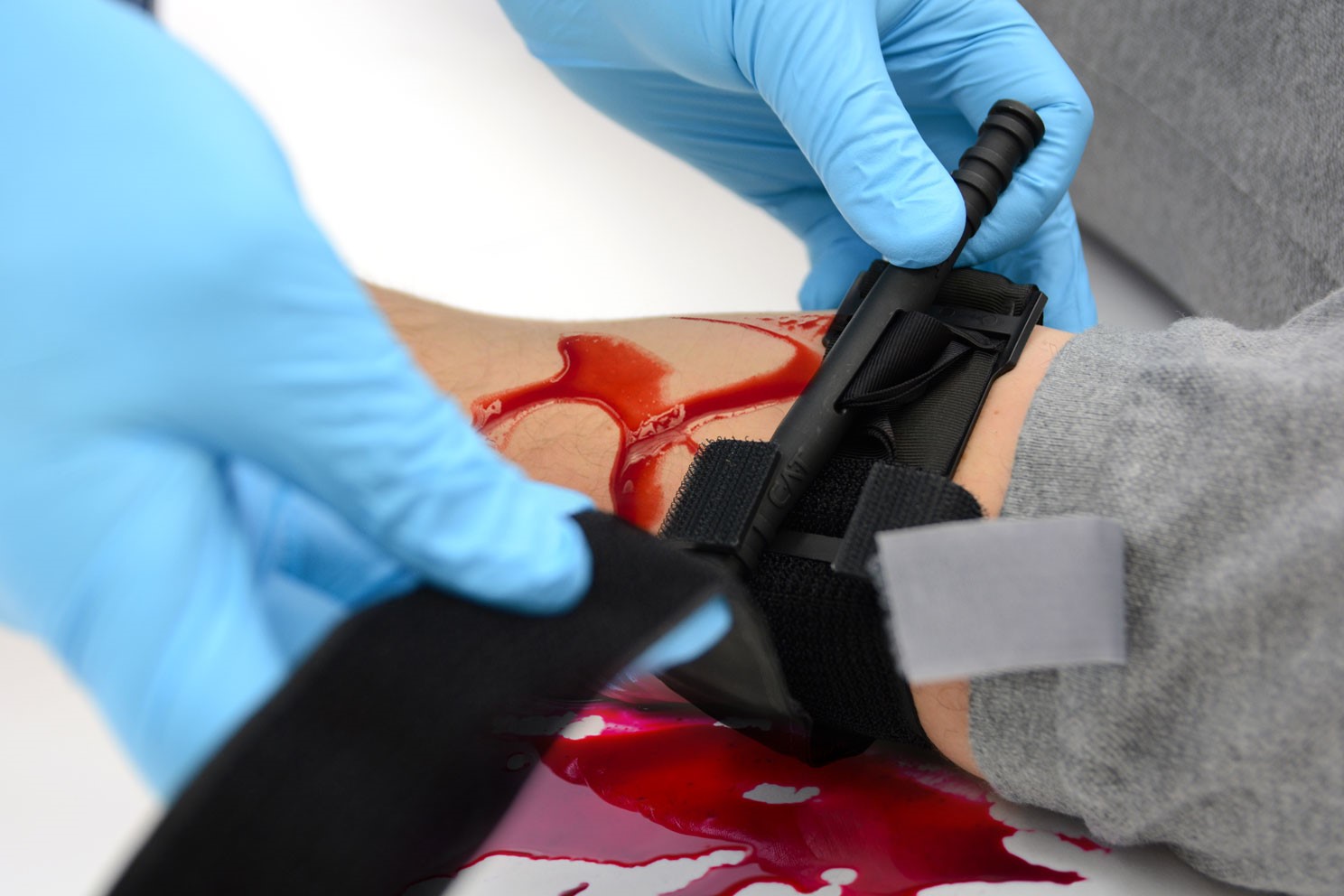
A tourniquet is one of the most important pieces of medical equipment in your first aid kit
Tourniquet is a tight band used to control bleeding by completely stopping the blood flow to a wound
Tourniquets work only on arm and leg injuries; you can’t exactly wrap a tight band around a patient’s neck and cinch it down to stop the flow of blood
Traditionally, tourniquets were reserved for the worst bleeding to keep the patient from developing shock.1
FIRST AID TRAINING? VISIT THE DMC DINAS MEDICAL CONSULTANTS BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
The Tourniquet Controversy
The use of tourniquets was first documented on the battlefield in 1674.
Complications of tourniquet use were said to lead to severe tissue damage.
Soldiers had amputations of limbs that were often attributed to the use of tourniquets but could have just as easily been from infection.
Eventually, tourniquets developed a bad rap in the field of emergency first aid.
Applying a tourniquet in the civilian world used to be seen as a last resort.
It was thought that they made sense for soldiers because combat wounds are severe and a fighter needs to fight.
It was a risk worth taking went the theory.
A tourniquet can be applied and ignored.
That doesn’t mean tourniquets don’t work.
On the contrary, tourniquets can arrest bleeding quite well and are certainly useful in cases of severe bleeding that cannot be stopped any other way.
They’re popular on the battlefield because they can be applied quickly and do not need to be constantly monitored once they are in place, allowing even injured soldiers to remain conscious and continue fighting.
Civilians, the thinking went, had time.
We could go methodically through steps to control bleeding.
We were taught to start with direct pressure and if that doesn’t work, elevate.
If the bleeding continued, a tourniquet became the dire option.
So maligned, tourniquets were thought to guarantee the loss of a limb if they were used.
Losing that blood flow would most certainly lead to catastrophic tissue damage.
Modern, evidence-based medicine is changing long-held views about tourniquets.
Hemorrhage is a serious issue.
When it’s present, it needs to be stopped.
If not, the patient could die. There’s no time to mess around.
When to Use a Tourniquet
Tourniquet application should happen in two cases:
- If bleeding can’t be stopped with direct pressure and elevation when both are applied immediately and simultaneously.
- If there’s any reason direct pressure can’t be maintained, even if it’s working.
Number 1 is the traditional view of going through the steps of bleeding control but accelerated.
Number 2 is a lesson learned from combat.
Fighters fight, and tourniquets let them.
That applies to civilians, too.
Hikers need to hike to get to help.
Patients with multiple injuries need treatments that allow the hands to be free.
Long waits for the ambulance lead to fatigue in the hands of the rescuer trying to hold direct pressure.
Tourniquets can also be self-applied by the patient.
Self-application of direct pressure is much harder.
THE RADIO OF THE WORLD’S RESCUERS? VISIT THE RADIO EMS BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT)
The combat application tourniquet (CAT) is the most common commercial tourniquet available.
It meets the requirements of the US military.
It won’t pinch, it uses a windlass (a handle to tighten the tourniquet), and it can be self-applied by the patient.2
The CAT should be prepared prior to use by feeding the tip of the strap through the friction buckle.
If you don’t, it could be very hard to do under stress in the heat of the moment, especially if you’re wearing gloves (nitrile or leather).
The only drawback to preparing the tourniquet in advance is that you then have to slip it over the extremity to get it into place.
Special Operations Force Tactical (SOFT) Tourniquet
The SOFTT is almost exactly the same as the CAT, except for the buckle.
The CAT has a friction buckle that can be cumbersome during use, especially if you’re wearing any sort of personal protective gloves.
The buckle on the SOFTT snaps together, which allows you to have the end of the strap already fed through the friction slide.
In this case, you don’t have to slip a circle of canvas strap over the end of the injured arm or leg.
You can simply wrap the tourniquet around the limb and snap it into place.
This functionality is only helpful if you’re applying the tourniquet to someone else.
As far as self-application goes, it’s nearly impossible to snap it together with one hand, so putting it on your own arm is the same as using the CAT.
SWAT-T
The SWAT-T is a different kind of tourniquet than either the CAT or the SOFTT.
Aimed more at civilian populations, it uses thick rubber to accomplish the same thing as the windlass does for the other two.
The SWAT-T can’t be self-applied, but unlike the CAT or the SOFTT, it can be applied to children and very small adults.2
Tourniquets with a windlass must have a pinch plate, a thick area of fabric below the windlass that blocks the skin from being pulled into the twisted strapping.
Without a pinch plate, skin and soft tissue can be twisted and pulled, causing pain, and in patients with delicate skin, further injury.
Pinch plates on the CAT and the SOFTT make it impossible for them to cinch down small enough for children and very small, usually elderly, adult patients.
An extra plus for small patients: the SWAT-T can be cut into two tourniquets for multiple injuries or multiple patients.
Common Tourniquet Mistakes
The most common problem with tourniquets is putting them on too loosely.
If a tourniquet isn’t so tight that it’s uncomfortable, it’s not working.
Improvised tourniquets have a very high failure rate, so you should always keep a commercial tourniquet in your first aid kit for severe bleeding.
More than one, in fact, because a single tourniquet—even when applied correctly—might not be enough to stop the bleeding.
Don’t be afraid to apply two or three tourniquets, especially on legs and to overweight patients.1
In addition to avoiding improper use of tourniquets, tourniquets should not be removed by anyone other than a doctor in the emergency department.
While leaving a tourniquet in place too long could theoretically lead to tissue damage, I was unable to find any documented cases of such damage and removal is very likely to lead to more severe bleeding.
Bibliographic references:
- Rowe B. Tourniquets in First Aid. Tourniquets in First Aid.
- American College of Emergency Physicians. Tactical Emergency Medicine.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Electric Shock First Aid And Treatment
The Patient Complains Of Blurred Vision: What Pathologies Can Be Associated With It?
T. Or No T.? Two Expert Orthopaedics Speak On The Total Knee Replacement
T. And Intraosseous Access: Massive Bleeding Management
Tourniquet, A Study In Los Angeles: ‘Tourniquet Is Effective And Safe’
Abdominal Tourniquet As An Alternative To REBOA? Let’s Find Out Together