Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
More often just called hidradenitis, hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammation of the hair follicle with characteristics similar to acne, first described by Alfred Velpeau in the 19th century
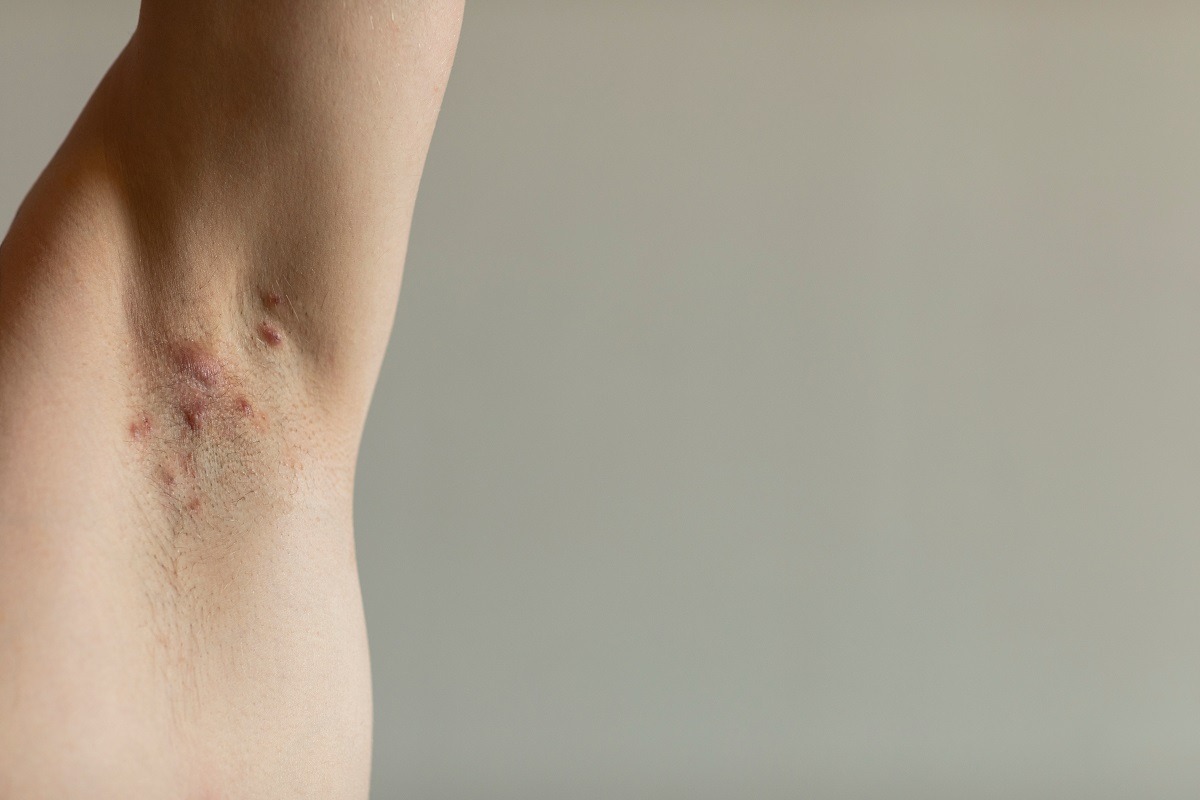
The subcutaneous nodules typical of the disease generally appear in the armpits, groin, between the buttocks and in the genital and perianal regions, for reasons that are currently unknown.
Although it is not well known, the first Italian Idradenitis Suppurativa Registry believes that a percentage of the population between 1 and 4% may suffer from it.
The incidence is three times higher among women than among men, and the age at which it is diagnosed is usually puberty.
What is hidradenitis suppurativa?
Chronic inflammation and scarring, hidradenitis suppurativa (or acne inversa) causes painful nodules that resemble skin abscesses.
Swollen and painful due to the inflammatory process affecting them, these formations can be minor (comedones, small cysts, light swelling) or appear as painful abscesses that secrete foul-smelling liquid.
The areas of the body most affected are the armpits, the area under the breasts, the groin and the perianal region.
Hidradenitis suppurativa occurs in several stages:
- phase 1 is the onset phase, characterized by the appearance of isolated nodules that are painful to the touch
- phase 2 (intermediate) sees the presence of multiple nodules, more painful and appearing more frequently
- phase 3 is the most serious phase, and is characterized by the onset of multiple nodules in multiple and organized anatomical districts with frequent leakage of pus
To date, the causes of hidradenitis suppurativa are poorly understood
According to the most recent studies, the pathology would be triggered by genetic and hormonal factors: it is in fact frequent that several subjects suffer from it within the same family nucleus, and a connection has been found between the worsening of the inflammation and the presence of androgen hormones (symptoms worsen before menstruation and after pregnancy, and ease while pregnant or after menopause).
Among the causes of hidradenitis suppurativa there are also the use of oral contraceptives, smoking and obesity, but also an abnormal response of the immune system (the disease is in fact more common among carriers of autoimmune diseases).
What is certain is that hidradenitis does not have an infectious origin, is not sexually transmitted and is not affected by hygienic habits.
Rather, it is more likely to be affected in case of familiarity or in conjunction with other pathologies such as arthritis, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity or severe acne.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of hidradenitis suppurativa is the appearance of nodules in specific regions of the body.
Generally, they initially manifest in a single anatomical area and then grow in quantity and also appear in the other regions where there are apocrine glands, subject to rubbing.
In each person, pathology manifests itself differently.
The nodules can appear as small swellings under the skin, be accompanied by isolated or multiple blackheads, result in red itchy papules which, if ruptured, produce foul-smelling pus or have the appearance of abscesses or pseudo-cysts.
Sometimes, in the most serious cases and in the armpits, they can connect to each other under the skin, giving rise to infected and very painful wounds.
During its third phase, the most serious, hidradenitis suppurativa can give rise to a series of complications.
Where the nodules appear, the emission of pus can cause skin infections.
Scars caused by subcutaneous fistulisation of the various nodules may also appear, and the pain can be so annoying as to make arm movements difficult (in the case of axillary nodules).
Finally, scar tissue can adhere to lymph nodes and cause problems with lymphatic drainage.
The evolution of hidradenitis suppurativa into a malignant tumor is very rare, although not excluded: in some patients, the nodules transform over time into squamous cell carcinomas.
On the other hand, the repercussions on private life are very frequent.
Suffering from depression and social isolation are two common tendencies among those affected by the disease in its most serious stages, because the nodules cause psychological discomfort and embarrassment.
Diagnosis
To prevent hidradenitis suppurativa from getting worse, it is essential that it is recognized and treated early.
It is therefore advisable to contact your doctor as soon as you notice the appearance of painful nodules in the anatomical districts mentioned and the pain does not disappear within fifteen days, but also if the appearance of nodules increases in frequency or the formations begin to affect different areas .
The doctor will essentially base himself on the observation of the nodules and the patient’s symptoms.
There is no ad hoc test for hidradenitis suppurativa: an objective examination and anamnesis are carried out by simply observing the formations and listening to the patient.
His family history will then be analysed, and his general health conditions will be checked.
Finally, the specialist will prescribe a series of blood tests to rule out the presence of an infectious disease for a differential diagnosis.
Hidradenitis suppurativa cannot be cured permanently
The prescribed therapies are aimed at controlling the symptoms, slowing down their progression and preventing complications from arising, so that the patient can live his life as normally as possible.
Pharmacological therapy is personalized on the individual patient and can include the administration of:
- oral or topical antibiotics, due to their antibacterial properties;
- oral corticosteroids or to be injected into the area of the nodules, used for their anti-inflammatory abilities, to be used for short periods due to their adverse effects on long-term therapies;
- retinoids (medicines used to treat acne);
- immunosuppressants, capable of reducing the autoimmune response where this is recognized as responsible for the manifestation of the disease;
- oral contraceptives, if symptoms worsen during the menstrual cycle;
- strong analgesics such as opioids and codeine, only in case of intractable pain.
If drug therapy does not give satisfactory results, surgical therapy can be used.
Likewise, surgery is considered when the nodules are multiple, when they have damaged skin tissue or cause excessively severe pain or frequent infections.
It is possible to proceed with the incision and drainage of the nodules, with the laser ablation of the same and their subcutaneous fistulas.
Nodules can also be removed with curettage followed by deroofing of the galleries, or with punch debridement (removal of torn or contaminated tissue).
On the other hand, tissue can be intervened with electrosurgery or with total surgical removal.
The prognosis depends on how early the diagnosis was and on the patient’s consistency in undergoing treatment.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Hyperhidrosis: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Eczema, Rash, Erythema Or Dermatosis: Let’s Talk About Our Skin
Pustular Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes And Remedies
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Definition, Causes And Treatment
Dermatosis: Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
Allergic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment And Prevention
Skin, What Are The Effects Of Stress
Eczema: Definition, How To Recognise It And Which Treatment To Favour
Dermatitis: The Different Types And How To Distinguish Them
Contact Dermatitis: Patient Treatment
Stress Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms And Remedies
Infectious Cellulitis: What Is It? Diagnosis And Treatment
Contact Dermatitis: Causes And Symptoms
Skin Diseases: How To Treat Psoriasis?
Eczema Or Cold Dermatitis: Here’s What To Do
Psoriatic Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Psoriatic Arthritis: How To Recognize It?
Skin Diseases: How To Treat Psoriasis?
Psoriasis, A Disease That Affects The Mind As Well As The Skin
Guttate Psoriasis: Causes And Symptoms
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Psoriasis: It Gets Worse In Winter, But It’s Not Just The Cold That’s To Blame
Childhood Psoriasis: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Treat It
Topical Treatments For Psoriasis: Recommended Over-The-Counter And Prescription Options
What Is Pustular Psoriasis? Definition, Causes, Symptoms And Treatment


