Pustular psoriasis: symptoms, causes and remedies
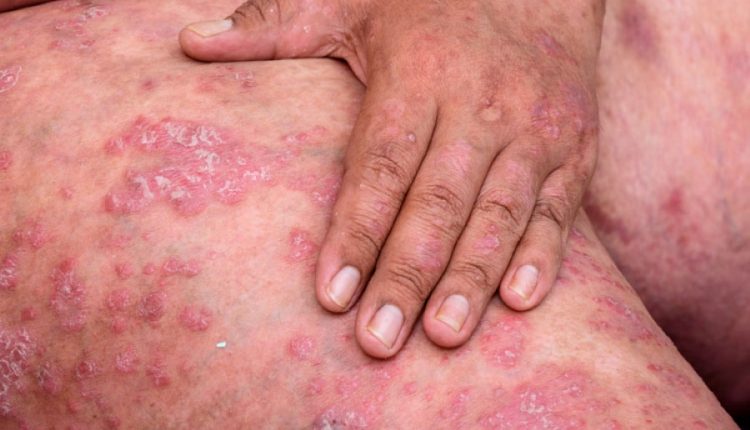
Pustular psoriasis is a skin disorder that can present in heterogeneous ways and is characterised by sterile pustules
The different forms of pustular psoriasis
The known clinical phenotypes of pustular psoriasis are:
- acute generalised pustular psoriasis (Von-Zumbusch’s)
- impetigo herpetiformis (typical of pregnancy);
- palmoplantar pustular psoriasis;
- pustular psoriasis annularis;
- infantile pustular psoriasis;
- continuous acrodermatitis of Hallopeau.
These different forms of psoriasis have in common, from a clinical point of view, the presence of sterile pustules (i.e. not due to bacterial infection) arising on an erythematous basis.
The symptoms with which it manifests itself
Symptoms vary from
- paucisymptomatic forms (few and of low intensity);
- forms that endanger the patient’s general condition (in the generalised form).
From a pathogenetic point of view, pustular psoriasis is characterised by an intense inflammatory response due to an exaggerated activation of innate immunity with a main involvement of interleukin 36.
Risk factors for pustular psoriasis
Although in some cases pustular psoriasis occurs without clear triggering causes, several risk factors have been described that can promote its onset, such as:
- medications;
- infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- excessive photo-exposure;
- cigarette smoking.
Diagnosis and therapy
The diagnosis can be made on the basis of the clinical-anamnestic picture and confirmed by a histological test in the more complex forms.
Therapy of localised forms is mainly based on the use of topical corticosteroids, vitamin D derivatives and emollients, as well as phototherapy in palmo-plantar forms.
For generalised forms or localised forms that are not responsive to the aforementioned treatments, therapy has historically been based primarily on the use of systemic drugs such as:
- acitretin;
- cyclosporine;
- methotrexate.
In recent years, however, the advent of biologic drugs (mainly anti-TNF-alpha, anti IL 12/23 and anti-IL 17) has enabled a further marked improvement in the management of this disease.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Psoriatic Arthritis: How To Recognize It?
Skin Diseases: How To Treat Psoriasis?
Psoriasis, A Disease That Affects The Mind As Well As The Skin
Guttate Psoriasis: Causes And Symptoms
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Psoriasis: It Gets Worse In Winter, But It’s Not Just The Cold That’s To Blame
Childhood Psoriasis: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Treat It
Topical Treatments For Psoriasis: Recommended Over-The-Counter And Prescription Options
What Are The Different Types Of Psoriasis?
Phototherapy For The Treatment Of Psoriasis: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Arthrosis Of The Hand: How It Occurs And What To Do
Arthrosis: What It Is And How To Treat It
Arthrosis: What It Is And How To Treat It
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Study Of Oral Therapy With Tofacitinib By Gaslini Of Genoa
Rheumatic Diseases: Arthritis And Arthrosis, What Are The Differences?
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Joint Pain: Rheumatoid Arthritis Or Arthrosis?
The Barthel Index, An Indicator Of Autonomy
What Is Ankle Arthrosis? Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis And Treatment
Unicompartmental Prosthesis: The Answer To Gonarthrosis
Knee Arthrosis (Gonarthrosis): The Various Types Of ‘Customised’ Prosthesis
Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment Of Shoulder Arthrosis



