What is an intensive care unit (ICU)? Some information for the citizen
Intensive care refers to the specialised treatment given to patients who are acutely unwell and require critical medical care
An intensive care unit (ICU) provides the critical care and life support for acutely ill and injured patients
Unless you are an emergency admission, you will need a referral from your doctor or specialist to be admitted to ICU.
Who is cared for in ICU (Intensive Care Unit)?
Patients may have a planned admission following surgery, an unexpected admission after an accident or be admitted because of a sudden and critical deterioration to their health.
ICU teams are multi-disciplinary, made up of highly skilled intensive care nurses, doctors and specialists trained in providing critical care for patients with a variety of medical, surgical and trauma conditions.
Some hospital ICUs specialise in providing care for particular health conditions or injuries including:
- major trauma
- severe burns
- respiratory failure
- organ transplants
- complex spinal surgery
- cardiothoracic surgery.
What to expect in ICU
ICU is one of the most critically functioning operational environments in a hospital.
Every ICU in a hospital has a different environment that will reflect the specialist medical and surgical procedures they perform.
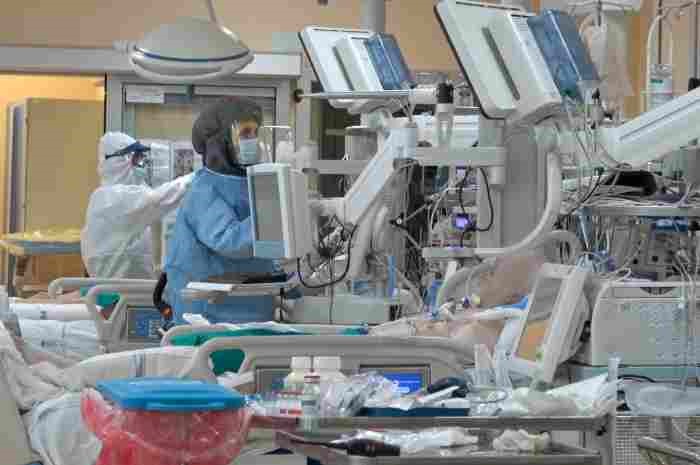
Most ICUs are fairly large sterile areas with a high concentration of specialised, technical and monitoring equipment needed to care for critically ill patients.
The ICU environment can be confronting for some patients and visitors who may find the activity, sounds, machines, tubes and monitors intimidating.
When you visit someone you care about in ICU it can be an uncomfortable experience – you may feel helpless, overwhelmed, frustrated and sad. Your feelings and apprehension are understood by the staff that provide support for the people you care about.
Typically ICU also has a higher ratio of doctors and nurses to patients.
Intensive Care Unit equipment
It can be a frightening and uncertain time for you, family and friends to see people you care about being monitored and supported by machines.
In ICU you will see many patients connected to a heart monitor, others will be supported with breathing assistance from artificial ventilators, be on dialysis machines and receiving a variety of intravenous infusions via tubes and drips.
Be prepared to see lots of lines, tubes, wires and monitoring equipment. Almost all ICU equipment uses alarms to let staff know about a change in a patient’s condition. Not all equipment alarms signal an emergency situation.
STRETCHERS, LUNG VENTILATORS, EVACUATION CHAIRS: SPENCER PRODUCTS ON DOUBLE BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Visitors
Every ICU has a visitor policy to ensure the wellbeing of their patients. You will need to ask ICU hospital staff about their specific visiting hours and requirements.
Visiting is usually restricted to people the patient considers to be immediate family.
If you are feeling unwell or have an existing health condition you should reconsider visiting ICU or discuss your circumstances with ICU staff before you plan to visit.
Hygiene
As intensive care patients are very vulnerable to infections, it is important that visitors wash their hands before entering ICU to prevent transferring infection.
Mobile phones
Mobile phones should be turned off in ICU as they may interfere with vital electrical equipment supporting patients.
Gifts
Restrictions are in place to allow easy access to vital medical equipment and to patients.
If you are unsure what you can bring with you check with ICU staff before you plan to visit.
Speak to ICU staff if you would like to use interpreting services.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Brain Monitoring Of The Newborn: What It Is And Why It Is Practised In Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): How Is A Score Assessed?
AED With Rain And Wet: Guideline To The Use In Particular Environment
Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale. Its Role In Emergency Department
How To Rapidly And Accurately Identify An Acute Stroke Patient In A Prehospital Setting?
Cerebral Haemorrhage, What Are The Suspicious Symptoms? Some Information For The Ordinary Citizen
When A Loved One Is In The Intensive Care Unit (ICU)