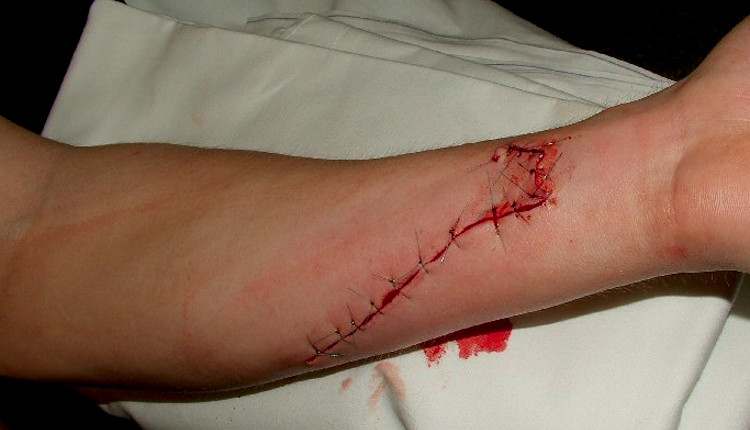
First Aid, How to Properly Dress a Wound
Properly dressing a wound is one of the most basic first aid techniques there is. The process remains unchanged regardless of the size or severity of the injury. Whether it’s a child’s skinned knee or a gunshot wound, the tenets of wound dressing are identical
Minor cuts and scratches can be treated at home or on the road.
Larger lacerations may also need to be dressed until medical help can be obtained.
Cleanliness is key.
RESCUE WORKERS’ RADIO IN THE WORLD? VISIT THE EMS RADIO BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Assess Bleeding
Coming in contact with someone else’s blood poses risks, such as transmitting certain diseases.
If at all possible, protect yourself by following universal precautions and wearing personal protective equipment (e.g., nitrile gloves or a mask).
Then, assess the bleeding. A little bleeding is okay because it helps flush dirt and other contaminants out of the wound, but heavy bleeding is bad.
Call Emergency Number if there’s:
- Bright red or squirting blood
- A puncture wound on the head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, or back is more than an inch deep
- A deep puncture wound on an arm above the elbow or a leg above the knee
Do what you can to stop the bleeding.
TRAINING: VISIT THE BOOTH OF DMC DINAS MEDICAL CONSULTANTS IN EMERGENCY EXPO
Clean the Wound
- Clean the wound with running water.1
- Wash the skin around the injury with soap. Don’t worry if soap gets into the wound, though it is likely to sting and irritate the raw tissue.
- Rinse the wound thoroughly to rid it of any dirt and soap.
- Use tweezers to remove particles (like broken glass or gravel).
Antibiotic ointment isn’t necessary for a wound to heal nicely.
However, it can help reduce the pain of raw injuries, such as abrasions.
Hydrogen peroxide also isn’t necessary for cleaning a wound and it can be harmful.
The bubbling action of hydrogen peroxide creates oxygen gas—more than the blood can handle.
That can lead to a gas embolism, which is potentially fatal.
Cover the Wound
- Only cover the wound if it’s likely to come in contact with clothing or dirt.2
- Adhesive bandages are the easiest way to cover most minor lacerations and abrasions.
- Cuts less than 2 centimeters long can be held closed with butterfly bandages.
- If the edges of a laceration are not easily pulled together, then the wound may need stitches.
Get Medical Help
Deep lacerations extend into the tissues below the skin.
If you can see layers of tissue along the sides of the laceration, it’s pretty deep.
Puncture wounds are harder to evaluate and should be based on how long the offending object is.
Seek medical attention for a deep wound if it’s:
- Tender or numb
- Inflamed (red and swollen)
- Draining pus (yellowish, thick liquid)
- A laceration with jagged edges or won’t close
Also, get medical help if it’s been more than five years since the victim had a tetanus shot.
References:
- Dreifke MB, Jayasuriya AA, Jayasuriya AC. Current wound healing procedures and potential care. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;48:651-62. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2014.12.068
- Dhivya S, Padma VV, Santhini E. Wound dressings – a review. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2015;5(4):22. doi:10.7603/s40681-015-0022-9
- American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD). Proper Wound Care: How to Minimize a Scar.
Additional Reading
- National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC). Guideline summary: SOLUTIONS® wound care algorithm. In: National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC) [Web site]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ); 2013
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
The Physiologic Response To Bleeding
Wound Infections: What Causes Them, What Diseases They Are Associated With
Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible Shock: What They Are And What They Determine
Drowning Resuscitation For Surfers
First Aid: When And How To Perform The Heimlich Maneuver / VIDEO
First Aid, The Five Fears Of CPR Response
Perform First Aid On A Toddler: What Differences With The Adult?
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
Chest Trauma: Clinical Aspects, Therapy, Airway And Ventilatory Assistance
Internal Haemorrhage: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Severity, Treatment
How To Carry Out Primary Survey Using The DRABC In First Aid
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Poison Mushroom Poisoning: What To Do? How Does Poisoning Manifest Itself?
Hydrocarbon Poisoning: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
First Aid: What To Do After Swallowing Or Spilling Bleach On Your Skin
Signs And Symptoms Of Shock: How And When To Intervene
Wasp Sting And Anaphylactic Shock: What To Do Before The Ambulance Arrives?
Spinal Shock: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prognosis, Death
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
KED Extrication Device For Trauma Extraction: What It Is And How To Use It
Introduction To Advanced First Aid Training
Drowning Resuscitation For Surfers
The Quick And Dirty Guide To Shock: Differences Between Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible
Dry And Secondary Drowning: Meaning, Symptoms And Prevention
First Aid: Definition, Meaning, Symbols, Objectives, International Protocols
First Aid: How To Help Someone With Stab Wounds


