How is eye pressure measured?
Eye pressure: measurement of intraocular pressure or tonometry is one of the main ophthalmological examinations
In healthy people, the pressure inside the eyeball should usually be in the range of 10-21 mmHg.
Increased intraocular pressure is the most important risk factor for glaucoma, a very serious disease that destroys the fibers of the optic nerve.
Progressive glaucoma is a common cause of complete blindness and is often completely asymptomatic.
Therefore, after 40 years, every person who visits an ophthalmologist should do tonometry.
How is eye pressure measured in adults?
Currently, there are three main methods by which the patient is measured intraocular pressure (IOP).
-
Applanation tonometry
It is considered one of the best and most accurate methods of studying the pressure inside the eyeball.
Its principle is based on the physical rule of Imbert-Fick.
It says that the pressure inside the sphere is equal to the force needed to smooth it, divided by the area of the smoothed surface.
Since the eyeball is a ball, this law allows you to determine the intraocular pressure.
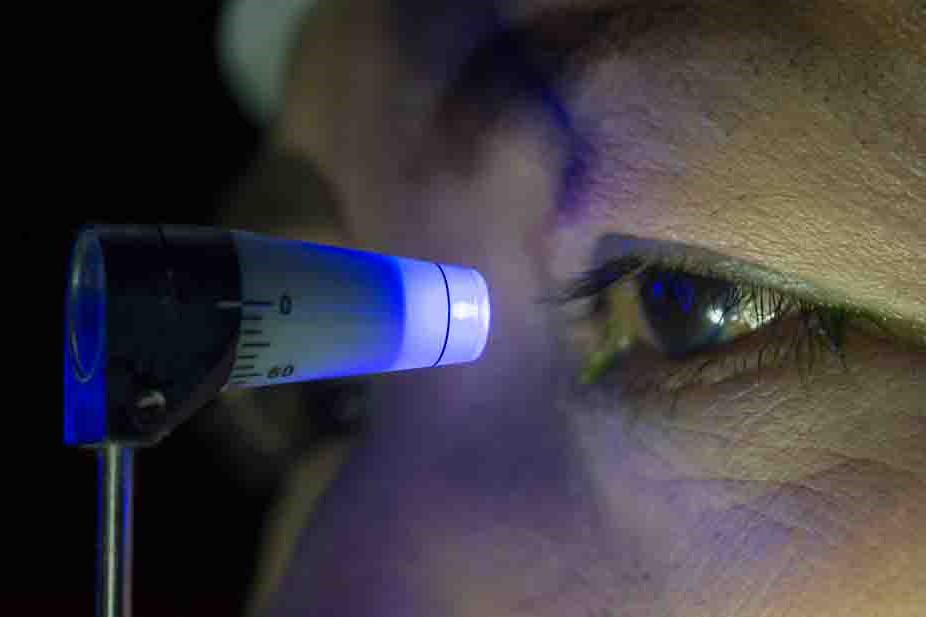
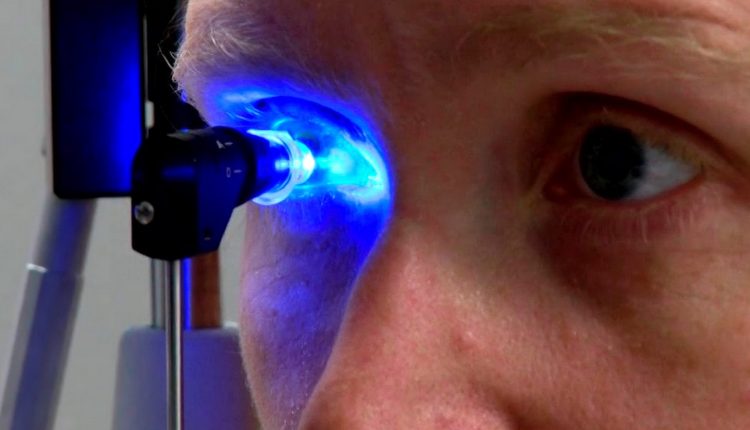
In applanation tonometry, the Goldman eye tonometer is used – a device equipped with a double prism with a diameter of 3.06 mm.
It is used for basic ophthalmological examination.
Before measuring IOP, the cornea is anesthetized with eye drops (local anesthesia), and the tear film is stained with a fluorescent solution that begins to glow (fluorescence) under the influence of cobalt-blue light.
Then the patient sits down in front of the slit lamp and rests his forehead on a special stand. You need to look directly at the indicator with your eyes wide open.
The tip of the prism is applied to the cornea.
Upon contact with the cornea, a colored film forms a meniscus around the diagnostic tip of the prism, which looks like two yellow semicircles.
An ophthalmologist looks through a microscope at a circle of tears stained with fluorescein.
Then a special pen increases the pressure on the cornea until an image of two S-shaped semicircles is obtained.
At this moment, knowing the surface area and the pressure force, the value of the intraocular pressure is read.
The reliability of the result may be influenced by the structure of the cornea.
This measurement method is not recommended for people with initially thick cornea, deformed surface or corneal edema.
-
Tonometry is contactless
This is a kind of applanation tonometry based on the same physical principle.
However, here a jet of compressed air is used to align the cornea.
Since no foreign body is in contact with the surface of the eye, local anesthesia is not required.
The test is also performed sitting, resting his forehead on a special stand.
Unfortunately, a sudden gust of air can provoke defensive reflexes in some people, which leads to erroneous measurements.
Therefore, non-contact tonometry is not recommended for the diagnosis and control of intraocular pressure in patients with pre-existing glaucoma.
-
Impression tonometry
This method is gradually falling out of use.
Here the examination is carried out in a lying position and analgesia of the cornea with drops for anesthesia is required.
It is necessary to ensure that the clothes do not put pressure on the neck, since pressure on the veins can distort the measurement results.
You need to look straight ahead.
The doctor opens the eyelid of the examined eye independently, trying not to pinch the eyeball.
He then places the Skiotz tonometer perpendicular to the cornea.
This is a small portable device. It is equipped with a 5.5 g pin, which always compresses the cornea with the same force.
Depending on the amount of intraocular pressure, the cornea is deformed to varying degrees.
The degree of corneal deformation is indicated by an arrow on the tonometer scale.
Based on this, the pressure inside the eyeball is calculated.
When the pressure is very high and the pin weight of 5.5 g does not deform the cornea, you can use a larger pin with a weight of 7.5 g or even 10 g.
When using this method, the stiffness of the eyeball may affect the reliability of the measurement.
In older people, the indicators are sometimes overestimated.
However, in patients with Graves’ disease or severe myopia, the results, on the contrary, may be somewhat underestimated.
Eye Pressure: How to properly prepare for the study?
There is no need to prepare specially for the examination.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to loosen the tight collar under the neck.
The subject should breathe calmly without holding his breath (Valsalva maneuver) and not squeeze his eyelids.
Another inexperienced eye should look straight ahead into the distance.
For tests requiring anesthesia of the surface of the eyeball, the patient should inform the doctor about a possible allergy to anesthetic drugs.
Before the examination, it is also necessary to remove contact lenses.
How is eye pressure measured in children?
The ICARE electronic eye tonometer is the fastest way to diagnose IOP shown to children.
It does not require the use of painkillers of local anesthesia, as in the study of other tonometers.
The device eliminates the risk of injury to the eyeball, so it is absolutely safe even for the youngest patients.
The principle of operation of the device consists in instant contact of the tonometer sensor with the cornea of the eye.
The moment of touch lasts for a fraction of a second and does not cause unpleasant sensations in the child.
The exact measurement results are stored in the device’s memory, and the data is displayed on the computer monitor screen, and the ophthalmologist immediately sees them.
Indications for tonometric examination
Tonometry is a part of a routine eye examination.
However, it is especially recommended in the case of glaucoma, ocular hypertension (or suspected of it), as well as during monitoring after operations on the eyeball.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- there is a strong redness of the eyes that persists for more than a day;
- visual acuity decreases;
- purulent discharge forms in the eye;
- inflammation of the vascular membrane of the eye appears;
- severe headache occurs, especially in the area of the eye socket.
The examination is also carried out for certain diseases, for example, such as diabetes mellitus, as well as as a result of an eye injury.
Possible complications after tonometry
In principle, tonometry is a safe test that rarely leads to complications.
In rare cases, the patient may experience temporary opacity or redness of the eye, as well as a sensation of a foreign body under the eyelid associated with a slight loss of corneal epithelium as a result of mechanical contact of the device with the eye.
Is it possible to measure eye pressure at home?
The study of eye pressure at home is carried out by palpation of the closed eyelid of the eyeball.
The index finger should be gently pressed on the eye.
If the intraocular pressure is increased, then a too elastic and hard ball will be felt.
When the IOP is lowered, the sclera is slightly squeezed and deformed.
Of course, this method does not provide accurate indicators (the norm of pressure inside the eye is 10-21 mm Hg).
However, with its help, you can carry out a primary diagnosis of the eyeball at home, which will give you a reason to contact an ophthalmologist for a more thorough measurement of IOP.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Pupillary Reflex To Light: Mechanism And Clinical Significance
4 Reasons To Seek Emergency Care For Vision Symptoms
Autoimmune Diseases: The Sand In The Eyes Of Sjögren’s Syndrome
Blepharoptosis: Getting To Know Eyelid Drooping
Corneal Abrasions And Foreign Bodies In The Eye: What To Do? Diagnosis And Treatment
Corneal Abrasions And Foreign Bodies In The Eye: What To Do? Diagnosis And Treatment
Wound Care Guideline (Part 2) – Dressing Abrasions And Lacerations
Contusions And Lacerations Of The Eye And Eyelids: Diagnosis And Treatment
Macular Degeneration: Faricimab And The New Therapy For Eye Health
First Aid For Dehydration: Knowing How To Respond To A Situation Not Necessarily Related To The Heat
Hydration: Also Essential For The Eyes
What Is Aberrometry? Discovering The Aberrations Of The Eye
Red Eyes: What Can Be The Causes Of Conjunctival Hyperemia?
What Is Corneal Abrasion And How To Treat It
Covid, A ‘Mask’ For The Eyes Thanks To Ozone Gel: An Ophthalmic Gel Under Study
Opening The Eyes Of The World, CUAMM’s “ForeSeeing Inclusion” Project To Combat Blindness In Uganda
What Is Ocular Pressure And How Is It Measured?