Medical thermography: what is it for?
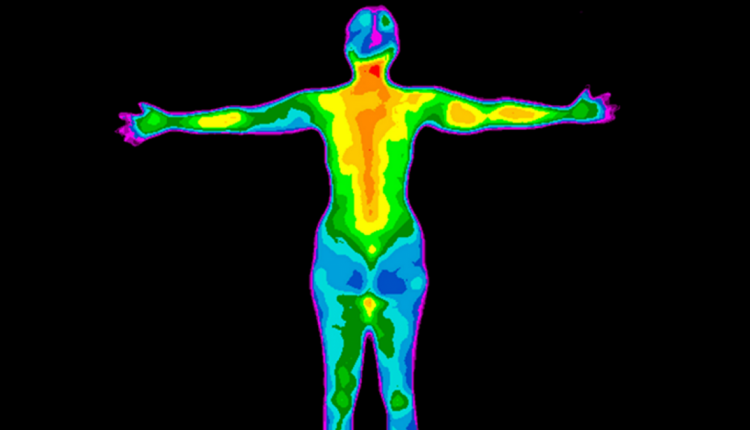
Medical thermography is a non-invasive technique that makes it possible to highlight and measure the surface temperatures of the human body, using the heat energy emitted by the body through the skin in the form of infrared electromagnetic radiation
When and how to perform medical thermography
The human body produces heat which, for the most part, is dispersed into the environment through the skin: thermography is based on the observation that various pathological processes cause an increase in heat production in the affected body region.
The thermographic examination is in fact used for the diagnosis of certain tumours (especially of the breast and thyroid) and inflammatory states of the muscular system or ischemic lesions.
It also makes it possible to assess changes in blood flow in the limbs.
Thermography is an examination with absolutely no side effects, it is painless, non-invasive, simple to perform and does not use harmful radiation.
THERMAL IMAGING CAMERAS FOR SAFE FIRE MANAGEMENT: VISIT THE HIKMICRO BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
There are different types of diagnostic investigation related to thermographic examination:
- Liquid crystal contact thermography: exploits the property of liquid crystals to change their spatial arrangement according to temperature: in practice, plates made of liquid crystals are placed on the skin of the area to be investigated and these take on a different colour depending on the skin temperature.
- Computer-assisted thermography: uses a plate that sends the different temperatures recorded on the analysed skin surface to a computer; the computer processes the data and provides an image consisting of the different colours corresponding to the different thermal gradations.
During medical thermography, the patient must be made comfortable in an environment with constant lighting
After taking the oral temperature (which must not exceed 37.5°C) the skin surface to be analysed must be exposed directly to the air for about 15 minutes.
The room temperature should be between 20° and 24°C, with relative humidity between 35 and 60%.
Prior to the examination, no smoking, no medication, no exposure to the sun or tanning lamps, no use of creams and refraining from strenuous physical activity.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Symptoms Of Emergencies In Children: Fever
Paediatric Seasonal Illnesses: Acute Infectious Rhinitis
Pediatrics: What To Do In Case Of High Fever In Children?
Paediatrics / Recurrent Fever: Let’s Talk About Autoinflammatory Diseases
Q Fever: What It Is, How To Diagnose It And How To Treat It
Respiratory Allergies: Symptoms And Treatment
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) Surge Serves As Reminder For Proper Airway Management In Children
Seasonal Illnesses: What To Eat When You Have Flu?
Fire Prevention: Hikvision Presents The Automation Thermographic Line
HIKMICRO Cameras: Thermal Imaging For Public Safety And Fire Prevention
London, Raging Fire In Dagenham Industrial Estate: 80 Firefighters And 12 Fire Engines At Work
HIKMICRO Thermography: Ensure Your Safety, Find Potential Risks



